10 types of fabric dyeing and printing techniques.
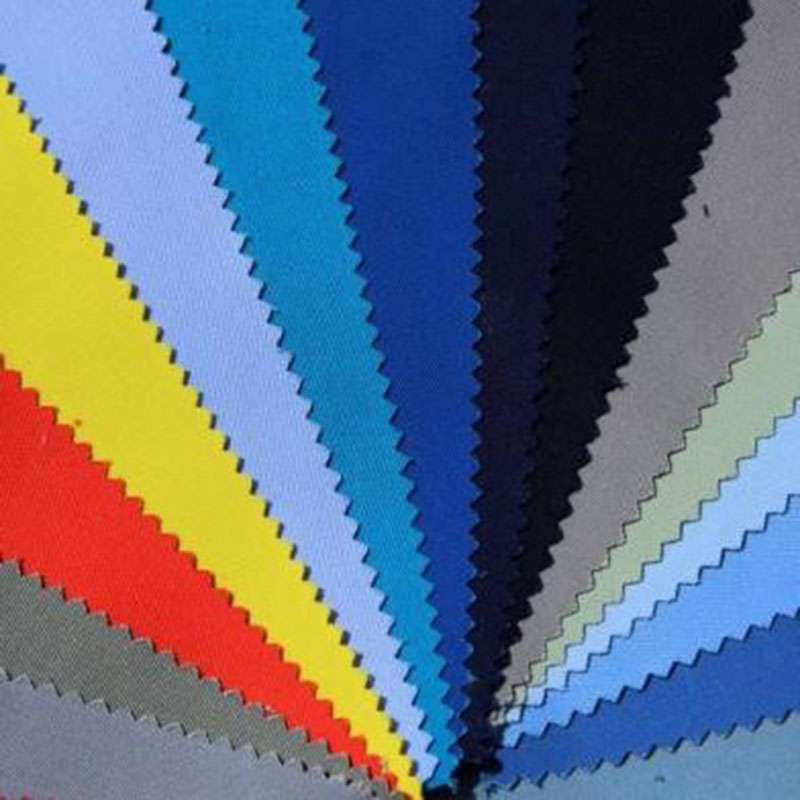
Plain Dyed
Solid color dyeing is a widely used technique where textiles are immersed in dye solutions to achieve uniform coloration. It is suitable for cotton, linen, silk, wool, and synthetic fibers. Key steps include fabric preparation, dye solution preparation, dye immersion, color fixation, and post-treatment. This method ensures high color fastness and versatility, commonly applied in clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics, producing vivid colors and excellent textures.


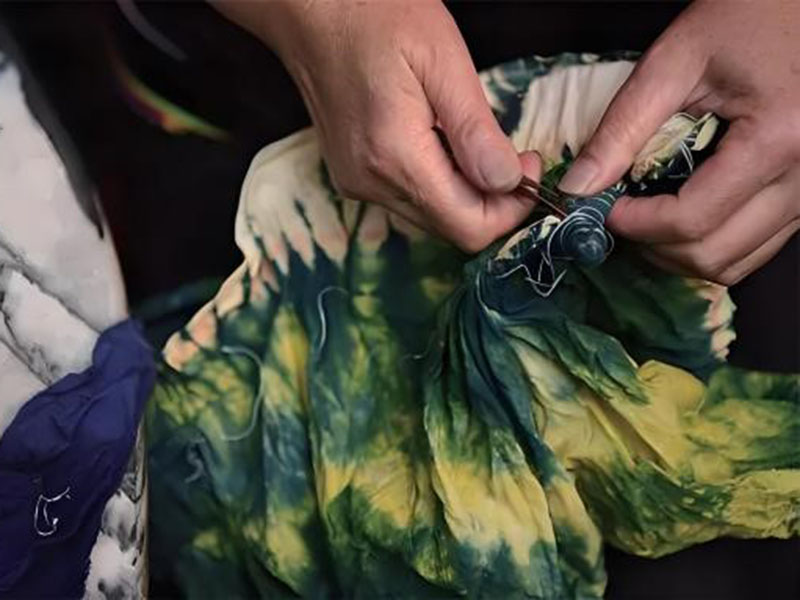
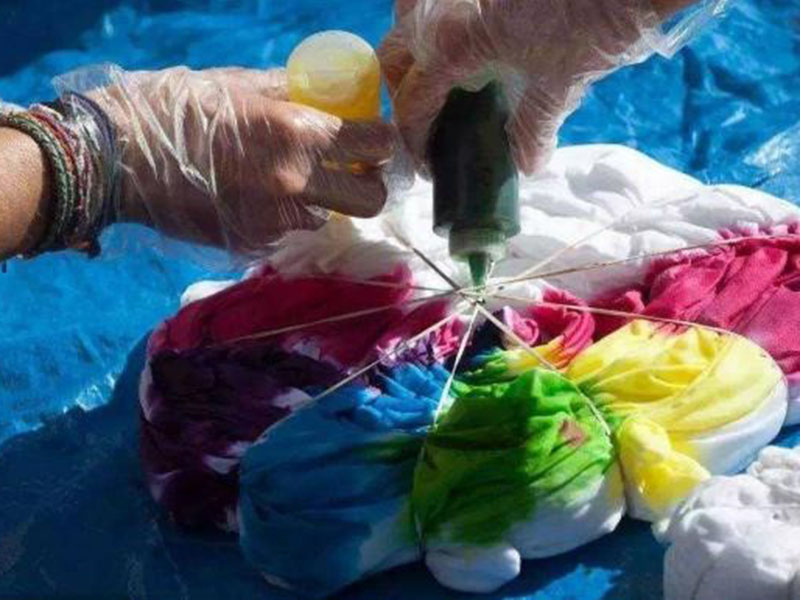
TIE DYED
Tie-dyeing is an ancient dyeing craft involving tightly tying or stitching sections of fabric to resist dye penetration, creating unique patterns and colors. Steps include designing tie-dye patterns, selecting dyes, immersion dyeing, multi-color dyeing, color fixation, washing, and finishing. Tie-dye patterns are distinctive and colorful, ensuring each piece is one-of-a-kind. Widely used in fashion, home textiles, and decorative items.


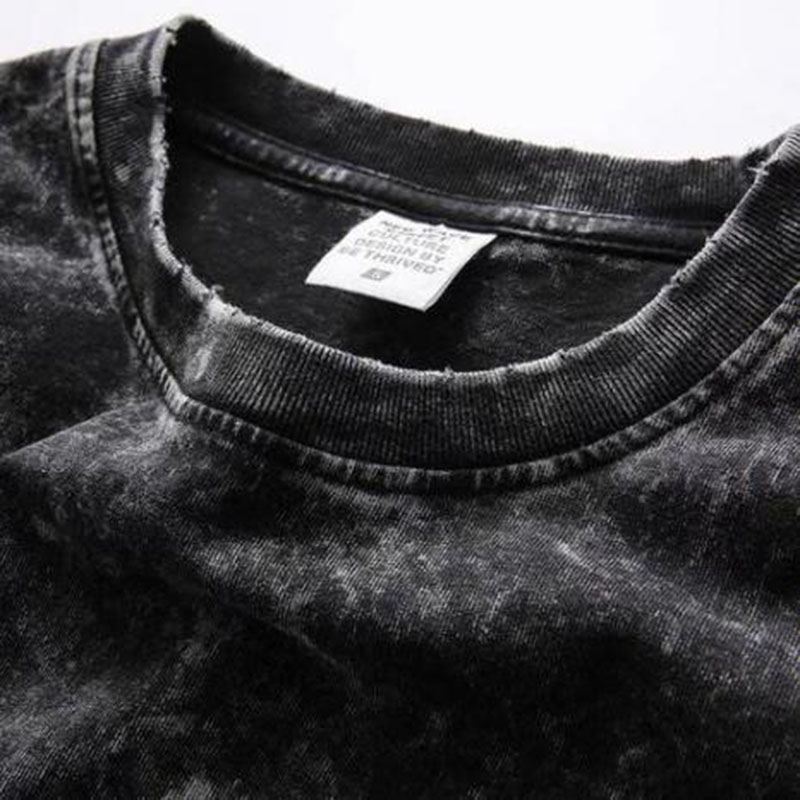
WASHED
Washing processes improve fabric hand feel, appearance, and comfort, suitable for cotton, denim, linen, and synthetic fibers. Main steps involve fabric selection, pretreatment, industrial washing machine cycles (cold, medium, or hot), and appropriate detergents. Techniques include enzyme wash, stone wash, and sand wash. Post-treatment includes color fixation, soft finishing, and drying, ensuring quality through ironing and quality checks. Washing processes enhance product texture and added value.
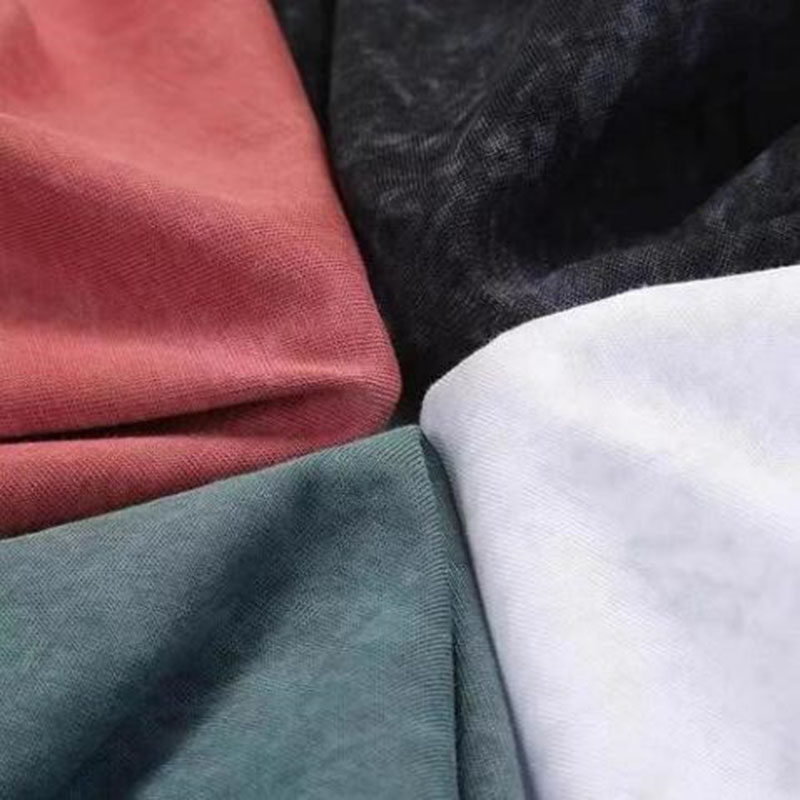


Color Blocked
Color blocking is a fashion design technique that creates sharp contrasts and striking visual effects by piecing together different colored fabrics. Designers select and coordinate colors, cut and assemble fabrics to ensure ideal proportions and placements of each color block. Beyond apparel, color blocking is widely used in home decor and artworks. Modern technologies such as digital printing and advanced cutting methods have made color blocking effects more intricate and precise, becoming an indispensable element in contemporary design.

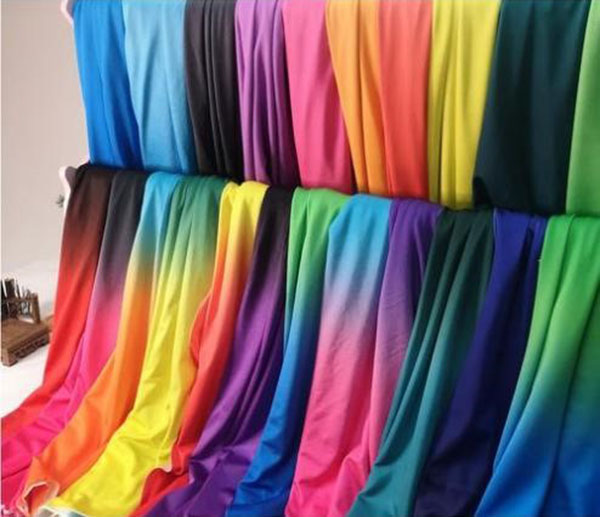
Gradient color
Gradient color is a design technique that achieves smooth and fluid visual transitions by gradually blending colors. It is widely applied in painting, digital art, fashion design, and handicrafts. Artists select colors and use tools like brushes, spray guns, or digital instruments to achieve natural gradient effects. Gradient colors enhance visual appeal and dynamics in artworks, creating smooth lines in fashion, emotional depth in paintings, and drawing attention in digital art, making it an essential element in artistic creation.

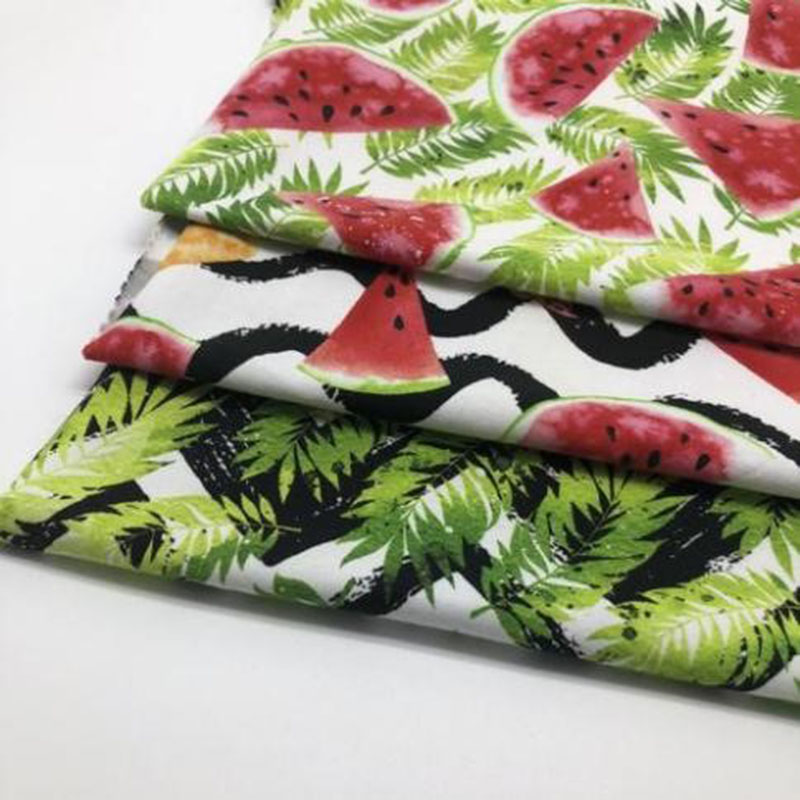
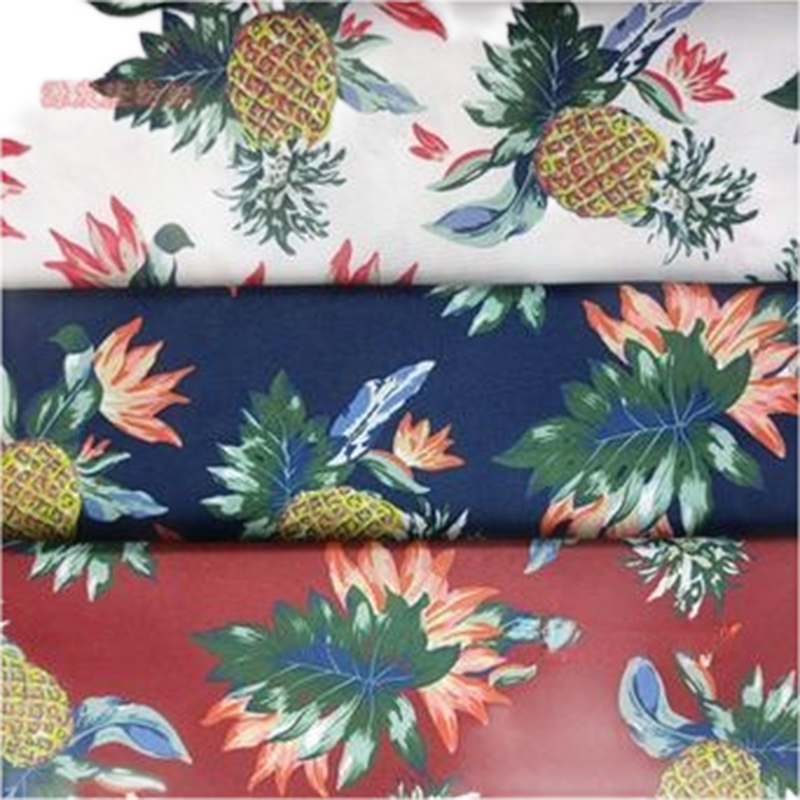
Digital Print
Digital printing is a modern printing technology that directly prints images on materials like fabric, paper, and plastic using computers and digital printers, achieving high-quality patterns and designs. Starting from digital design, it utilizes inkjet or UV technology to precisely control details. Digital printing requires no plates, has short production cycles, and adapts well, widely applied in fashion, home decor, advertising, and art. Its environmental benefits reduce chemical solvents and water use, combining technological innovation with environmental awareness, showcasing the limitless potential of digital printing.


Plain embroidery
Embroidery is an ancient and intricate handicraft creating intricate patterns and decorations through manual weaving. Artisans choose suitable fabrics and threads, using various stitching techniques based on designs ranging from simple lines to complex floral motifs, animals, and more. Embroidery is not just an art form but also carries cultural heritage and personal expression. Despite advancements in technology enhancing efficiency, embroidery remains favored by artists and enthusiasts, embodying traditional lifestyles and values.


Metallic Foil Screen Print
Hot foil stamping is a highly decorative technique that uses heat and metallic foil to imprint patterns or text onto surfaces. It enhances products with a luxurious metallic sheen and visual appeal, elevating their quality and sophistication. In the production process, designers prepare patterns and use specialized equipment to adhere heat-sensitive metallic foils to target surfaces, securing them through heat and pressure. Widely used in high-end packaging, exquisite gifts, luxury books, and premium brand promotional materials, hot foil stamping showcases exceptional craftsmanship and distinctive brand identity.

Heat Transfer Print
Heat transfer printing is a printing technique that transfers designs from transfer paper to surfaces using heat energy, extensively applied in clothing, home goods, and advertising materials. Designers first print patterns on specialized transfer paper and then transfer them to target objects via heat pressing, creating durable, high-quality, and diverse designs. This technology is versatile, unaffected by surface texture or shape, suitable for both flat and three-dimensional objects, supporting personalized customization and small-batch production, enhancing market competitiveness and brand image.


Silicone Printing
Silicone printing utilizes advanced silicone ink to print on various materials, enhancing durability, slip resistance, or decorative effects. Designers create patterns, select silicone ink, and apply it to the surface of target objects using screen printing or brush tools. After curing, silicone ink forms a robust coating suitable for sports apparel, industrial products, and medical devices, enhancing functionality and safety. Known for its durability, environmental friendliness, and ability to achieve intricate details, silicone printing injects innovation and market competitiveness into product design.